Title: Unmasking Acne: A Comprehensive Guide to Diagnosis and Treatment
As a medical professional, I’ve encountered countless patients struggling with the physical and emotional effects of acne. This common skin condition, affecting millions worldwide, can be a source of significant distress. But understanding acne’s causes, diagnosis, and treatment options can empower individuals to take control of their skin health. In this article, we will unmask acne, providing a comprehensive guide to its diagnosis and treatment.
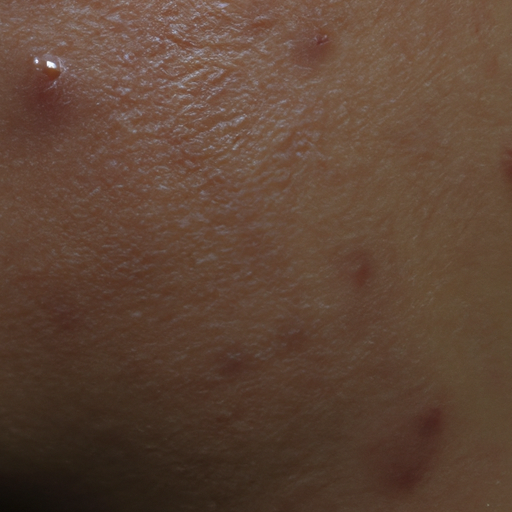
Acne is a skin condition that occurs when hair follicles become clogged with oil and dead skin cells. It is most common among teenagers, but it can affect people of all ages. Acne can appear on various parts of the body, including the face, back, and chest. Its severity can range from mild to severe, with symptoms including whiteheads, blackheads, pimples, cysts, and nodules.
Diagnosing acne is typically straightforward. As a doctor, I look for the telltale signs such as redness, inflammation, and the presence of comedones (blackheads and whiteheads). In some cases, I may refer patients to a dermatologist for further evaluation.
Understanding the root causes of acne is crucial for effective treatment. Hormonal changes, certain medications, diet, stress, and genetics can all contribute to acne development. However, contrary to popular belief, poor hygiene or eating greasy foods does not cause acne.
When it comes to treating acne, there’s no one-size-fits-all solution. The best treatment plan depends on the patient’s age, acne severity, and overall health. Over-the-counter (OTC) products containing salicylic acid or benzoyl peroxide can be effective for mild acne. These ingredients work by reducing inflammation and fighting bacteria.
For moderate to severe acne, prescription medications may be necessary. Topical retinoids are often the first line of treatment. They work by preventing the clogging of hair follicles. Other options include oral antibiotics, hormonal therapies (for women), and isotretinoin for severe cases.
In addition to medical treatments, lifestyle changes can also help manage acne. Maintaining a healthy diet, regular exercise, adequate sleep, and stress management can all contribute to improved skin health.
Lastly, it’s important to remember that acne treatments take time to work. Patience is key. It can take 6 to 8 weeks to see noticeable improvement, and your skin may even appear to get worse before it gets better.
In conclusion, acne is a common but treatable skin condition. Understanding its causes and treatment options can help individuals navigate their journey towards clearer skin. Remember, if you’re struggling with acne, you’re not alone, and help is available. Consult with a healthcare professional or dermatologist to find the best treatment plan for you.
Keywords: acne, skin condition, diagnosis, treatment, hair follicles, inflammation, comedones, hormonal changes, salicylic acid, benzoyl peroxide, topical retinoids, isotretinoin, lifestyle changes, skin health.