Title: Unmasking Acne: A Comprehensive Exploration of Symptoms and Causes
Acne, a common skin condition that affects millions worldwide, is often misunderstood and misdiagnosed. This article aims to unmask acne, delving deep into its symptoms and causes, providing a comprehensive understanding of this prevalent skin issue.
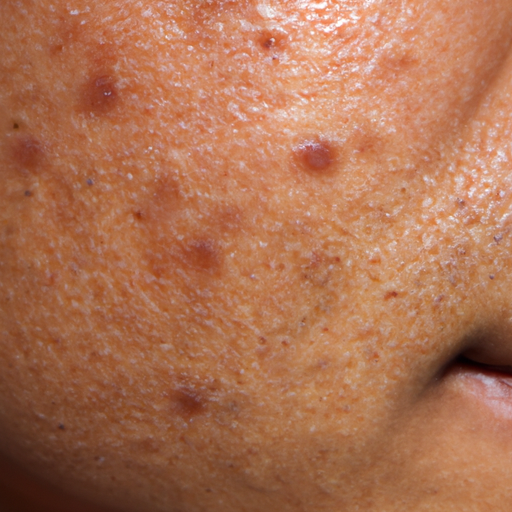
Acne is not just a teenage problem; it can affect people of all ages. It manifests as different types of blemishes on the skin, including whiteheads, blackheads, papules, pustules, nodules, and cysts. These blemishes typically appear on the face, neck, back, chest, and shoulders where the skin has the most oil (sebaceous) glands.
The most common symptom of acne is the appearance of these blemishes. However, acne can also cause discomfort such as tenderness or pain, and in severe cases, it can lead to scarring. It’s essential to understand these symptoms to identify acne accurately and seek appropriate treatment.
Now, let’s delve into the causes of acne. The primary cause is the overproduction of oil and the buildup of dead skin cells in hair follicles. When these elements mix, they create a perfect environment for Propionibacterium acnes (P. acnes), a bacteria that lives on our skin, to multiply. This bacterial growth leads to inflammation and the formation of acne blemishes.
Hormonal changes are another significant factor in acne development. During puberty, the increase in androgens (male hormones present in both males and females) causes the sebaceous glands to enlarge and produce more sebum (oil). Similarly, hormonal changes during pregnancy or when using oral contraceptives can also trigger acne.
Certain medications such as corticosteroids, lithium, or drugs containing testosterone may also cause acne. Moreover, diet plays a role too. Some studies suggest that consuming dairy products and carbohydrate-rich foods—such as bread, bagels, and chips—might trigger acne. Stress doesn’t cause acne directly, but it can worsen the condition in people who already have it.
Contrary to popular belief, poor hygiene or cosmetics do not cause acne. However, if you have acne-prone skin, using non-comedogenic products (products that do not block pores) can help prevent breakouts.
Understanding the symptoms and causes of acne is the first step towards effective treatment. If you’re struggling with acne, remember that you’re not alone, and there are numerous treatments available. Consult a dermatologist to discuss your symptoms and find a treatment plan that works best for you.
In conclusion, unmasking acne involves understanding its symptoms—such as the appearance of various types of blemishes and skin discomfort—and recognizing its causes, including overproduction of oil, buildup of dead skin cells, hormonal changes, certain medications, and diet. With this knowledge, you can take proactive steps towards managing your acne and achieving healthier skin.
Keywords: Acne, Symptoms of Acne, Causes of Acne, Skin Condition, Blemishes, Sebaceous Glands, Propionibacterium acnes, Hormonal Changes, Diet, Non-comedogenic Products, Treatment for Acne.